Customized optics aspheric glass pmma pc lenses of Plano-Convex(PCX) Double-Convex(DCX) Plano-Concave(PCV) Double-Concave(DCV)
Optical lenses are fundamental components in photonics, astronomy, microscopy, and laser systems. This guide delves into four core lens types—Plano-Convex (PCX), Double-Convex (DCX), Plano-Concave (PCV), and Double-Concave (DCV)—exploring their design principles, technical specifications, and applications.
1. Plano-Convex (PCX) Lenses
PCX lenses feature one flat surface and one convex surface, designed to focus parallel light into a single point with minimal spherical aberration when the convex side faces the incoming beam 1. Constructed from materials like BK7 glass or fused silica, they excel in applications requiring beam collimation, such as laser diode systems and barcode scanners. Coating options include UV, VIS, and NIR anti-reflective (AR) layers to enhance transmission efficiency 8.
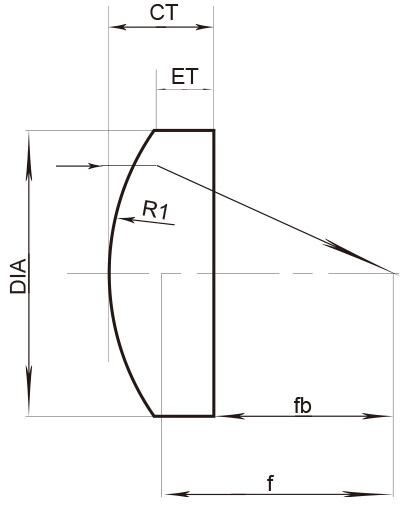
2. Double-Convex (DCX) Lenses
With two symmetric convex surfaces, DCX lenses exhibit positive focal lengths and are ideal for 1:1 imaging systems, where object and image distances are equal. Their symmetrical design minimizes spherical and coma aberrations, making them critical in microscopy and telescope objectives 2. DCX lenses are often paired with other optics to correct chromatic aberrations in complex systems.
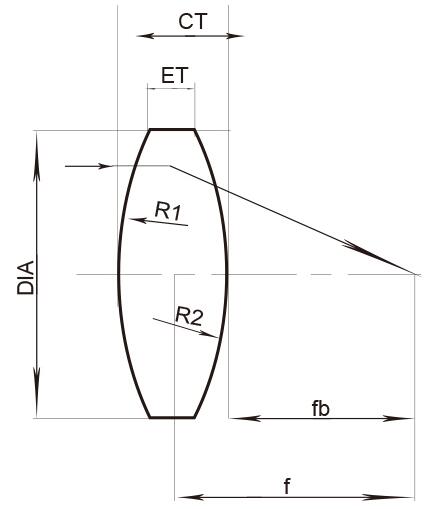
3. Plano-Concave (PCV) Lenses
PCV lenses combine a flat surface with a concave surface, producing divergent beams and negative focal lengths. They are used to expand light or reduce convergence in systems like fiber-optic collimators and beam expanders. PCV lenses also compensate for positive aberrations in multi-lens assemblies 2. Common materials include K9 glass and UV-grade fused silica.
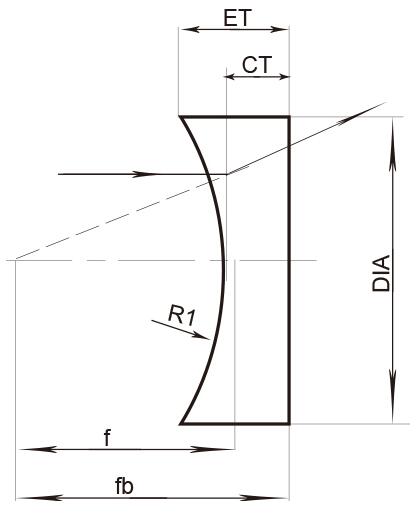
4. Double-Concave (DCV) Lenses
DCV lenses feature two concave surfaces, maximizing beam divergence while minimizing spherical aberration. They are essential in applications requiring uniform light distribution, such as projection systems and laser beam shaping. DCV lenses are often coated with SWIR AR films for infrared spectroscopy 7.
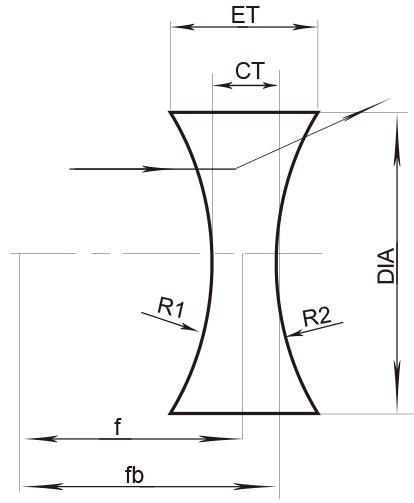
5. Meniscus lenses
Meniscus lenses are convex-concave lenses. They have one outward curved face and one inward-curved face. If the outward curve is sharper than the inward curve, the lens has a positive focal length and acts as a magnifier
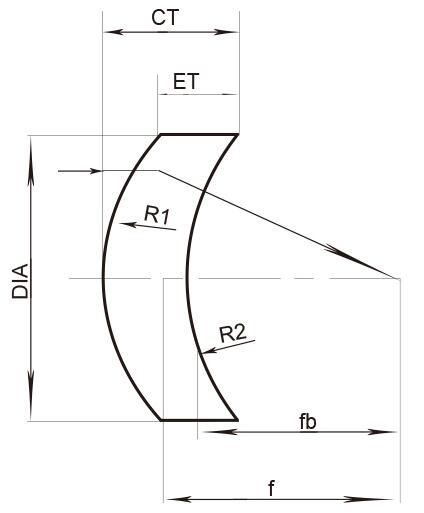
Technical Specifications & Material Selection
-
Materials: BK7 (visible spectrum), fused silica (UV/IR), and calcium fluoride (broadband UV-IR) are standard choices 21.
-
Coatings: AR coatings reduce reflection losses to <0.2% per surface, while high-reflection coatings enable beam steering 8.
-
Tolerances: Surface accuracy (λ/4 at 632.8 nm) and centration (<3 arcminutes) ensure precision in critical applications 21.
Applications Across Industries
-
Laser Technology: PCX lenses collimate laser diodes, while DCV lenses expand Gaussian beams.
-
Medical Imaging: DCX lenses enhance resolution in endoscopic systems.
-
Astronomy: PCV lenses correct aberrations in telescope eyepieces.
-
Consumer Electronics: Miniaturized PCX lenses are used in smartphone cameras 9.